LMCache KV cache存储
LMCache KV cache存储
Ref
https://github.com/LMCache/LMCache
LMCache | LMCache blog website
CS107, Lecture 24 - Explicit Free List Allocator
Shaping NIXL-based PD Disaggregation in vLLM V1 | LMCache blog website
Bringing State-Of-The-Art PD Speed to vLLM v1 with LMCache | LMCache blog website
Extending LMCache Remote Connectors: MooncakeStore as an Example | LMCache blog website
LMCache框架概览
LMCache当前的两个功能
1. Storage: DB-Style Loading and Offloading
支持KV cache从GPU offload到local CPU/Disk,以及通过remote接口offload到mooncake store等存储。然后可以基于offload结果加载prefix cache到GPU。相比于仅仅依赖GPU内存进行prefix cache存储,可以显著扩大prefix cache存储容量和命中率。
offload example:
LMCache/examples/kv_cache_reuse/
vllm serve with offload example:
export LMCACHE_CONFIG_FILE=lmcache-config.yaml
vllm serve Qwen/Qwen3-32B-FP8 \
-tp 8 \
--no-enable-prefix-caching \
--kv-transfer-config '{"kv_connector":"LMCacheConnectorV1","kv_role":"kv_both"}'配置文件设置见下面章节。
2. Transport: P2P-Style Direct Transfer
支持P/D之间基于NIXL的KV cache传输。内部构建了一个buffer区域,先从GPU拷贝到buffer,然后基于buffer进行NIXL传输,这样一定程度上可以避免KV cache的碎片化传输。
LMCache的一个大概架构图
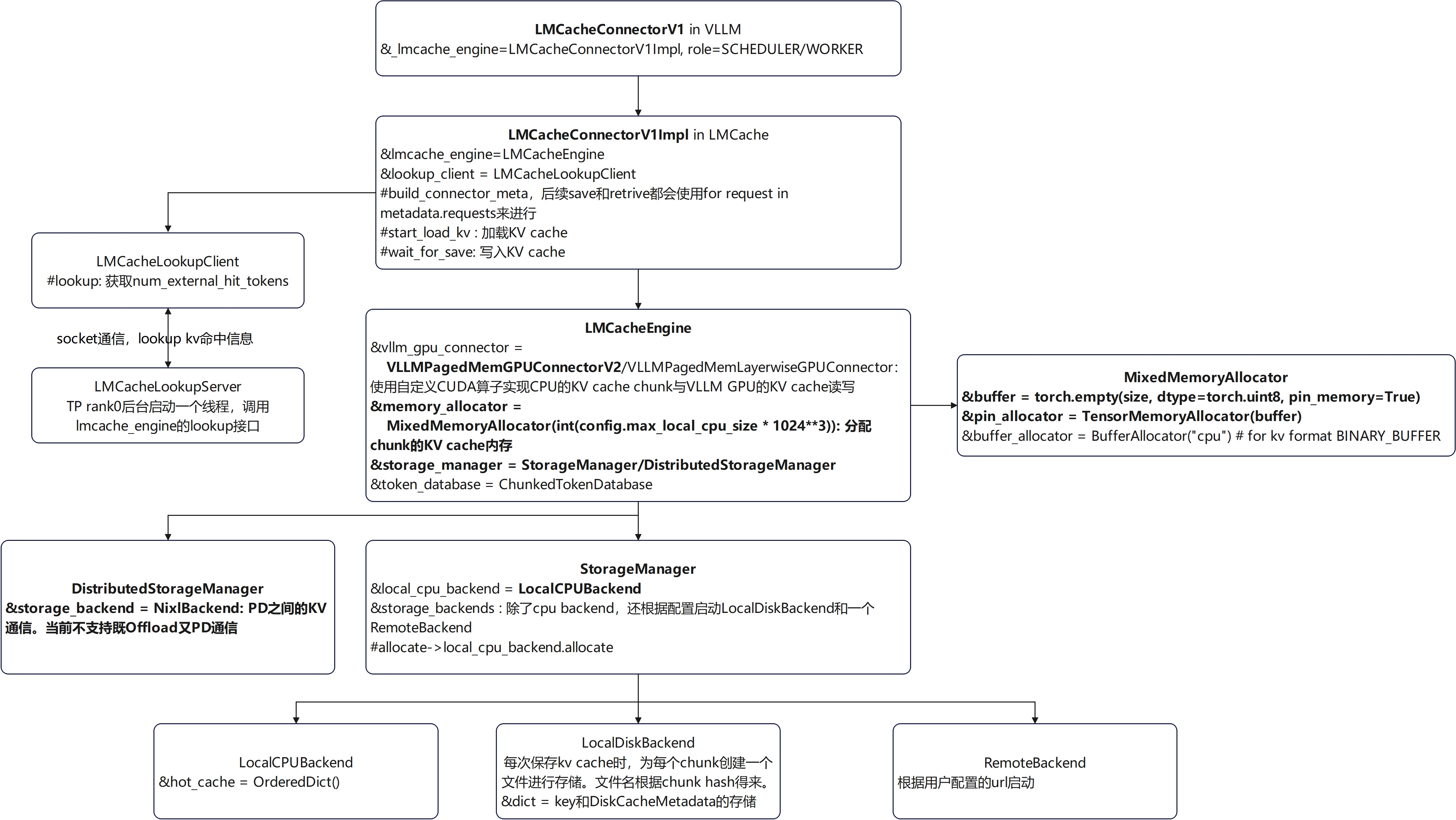
LMCache里面有一些CacheBlend相关的代码,这个是针对RAG场景的特殊优化,这个应该还需要上层框架和算法做一些配合。只看KV offload和传输的话,Blend关键字相关的可以完全忽略。
详解 CacheBlend:RAG 场景 KV 复用,打破前缀相同的限制
VLLM V1对LMCache的调用
Scheduler里面创建了一个connector,role是KVConnectorRole.SCHEDULER:
self.connector = KVConnectorFactory.create_connector_v1(
config=self.vllm_config, role=KVConnectorRole.SCHEDULER)sheduler里面的connector调用:
self.connector.get_num_new_matched_tokens() # can_load = False
self.connector.update_state_after_alloc() # set LMCacheConnectorV1Impl.load_specs[request.request_id].can_load = True
meta = self.connector.build_connector_meta(scheduler_output)GPU Worker里面通过ensure_kv_transfer_initialized创建了role为worker的connector:
_KV_CONNECTOR_AGENT = KVConnectorFactory.create_connector_v1(
config=vllm_config, role=KVConnectorRole.WORKER)Worker GPUModelRunner里面的connector调用:
kv_connector = get_kv_transfer_group()
kv_connector.bind_connector_metadata()
kv_connector.start_load_kv(get_forward_context())
get_kv_transfer_group().clear_connector_metadata()
get_kv_transfer_group().wait_for_save()
get_kv_transfer_group().get_finished()
get_kv_transfer_group().register_kv_caches(kv_caches)LMCache load/store
VLLM的调用
class GPUModelRunner(LoRAModelRunnerMixin):
@torch.inference_mode()
def execute_model()
# Run the decoder.
# Use persistent buffers for CUDA graphs.
with set_forward_context(attn_metadata,
self.vllm_config,
num_tokens=num_input_tokens,
num_tokens_across_dp=num_tokens_across_dp):
# load kv cache
self.maybe_setup_kv_connector(scheduler_output)
model_output = self.model(
input_ids=input_ids,
positions=positions,
intermediate_tensors=intermediate_tensors,
inputs_embeds=inputs_embeds,
)
# store kv cache
self.maybe_wait_for_kv_save()
finished_sending, finished_recving = self.get_finished_kv_transfers(scheduler_output)
LMCache prefetch调用链路
File "site-packages/vllm/v1/worker/gpu_worker.py", line 293, in execute_model
output = self.model_runner.execute_model(scheduler_output,
File "site-packages/vllm/v1/worker/gpu_model_runner.py", line 1258, in execute_model
self.maybe_setup_kv_connector(scheduler_output)
File "site-packages/vllm/v1/worker/gpu_model_runner.py", line 1540, in maybe_setup_kv_connector
kv_connector.start_load_kv(get_forward_context())
File "site-packages/vllm/distributed/kv_transfer/kv_connector/v1/lmcache_connector.py", line 48, in start_load_kv
self._lmcache_engine.start_load_kv(forward_context, **kwargs)
File "site-packages/lmcache/integration/vllm/vllm_v1_adapter.py", line 496, in start_load_kv
ret_token_mask = self.lmcache_engine.retrieve(
load的时间节点:only load KV for new requests,scheduler分配kv block之后。
LMCache store调用链路
File "site-packages/vllm/v1/worker/gpu_worker.py", line 293, in execute_model
output = self.model_runner.execute_model(scheduler_output,
File "site-packages/vllm/v1/worker/gpu_model_runner.py", line 1267, in execute_model
self.maybe_wait_for_kv_save()
File "site-packages/vllm/v1/worker/gpu_model_runner.py", line 1545, in maybe_wait_for_kv_save
get_kv_transfer_group().wait_for_save()
File "site-packages/vllm/distributed/kv_transfer/kv_connector/v1/lmcache_connector.py", line 88, in
self._lmcache_engine.wait_for_save()
File "site-packages/lmcache/integration/vllm/vllm_v1_adapter.py", line 697, in wait_for_save
self.lmcache_engine.store(
store时间节点:也是prefill计算后通常会store,后续decoding不是每一次都store,会检查是否超过lmcache_chunk_size的整数倍。
load和store的信息是在LMCacheConnectorV1Implbuild_connector_meta里面控制的。
chunk size
store,retrive,loopup是按lmcache的chunk size(默认为256)进行存储和检索的,这个独立于vllm的block size(通常默认为16)。这两个不一定需要相等,但是chunk size应该需要是block size整数倍。
for start, end, key in self.token_database.process_tokens(tokens, mask):start, end, key样例:
256, 512, CacheEngineKey(fmt='vllm', model_name='Qwen3-32B-FP8', world_size=1, worker_id=0, chunk_hash='54de13')
5888, 6005, CacheEngineKey(fmt='vllm', model_name='Qwen3-32B-FP8', world_size=1, worker_id=0, chunk_hash='4caecb')process_tokens返回的start, end, key是chunk的其实和结束id以及token的hash。输入token不足一个chunk的部分也被返回了。但是那末尾非chunk size整数倍的基本上被匹配的概率很小,除非是一模一样的请求,即使前缀相同也不行。所以这个部分不存储应该也是可以的。
LMCache存储按chunk来存,MHA的数据格式为
KV_2LTD: [2, num_layers, num_tokens, hidden_dim]
也就是所有layer一起打包存储了。
KV load内存操作
GPU和LMCache的内存之间是怎么进行拷贝的?
load的token数量是根据vllm自身匹配的部分进行处理:
masked_token_count = request.load_spec.vllm_cached_tokens // self._lmcache_chunk_size * self._lmcache_chunk_size
token_mask[:masked_token_count] = False
ret_token_mask = self.lmcache_engine.retrieve(tokens, token_mask, kvcaches=kvcaches, slot_mapping=slot_mapping,)
# Check the result
num_retrieved_tokens = ret_token_mask.sum().item()这个判断逻辑稍微有点粗糙(可能的优化:因为chunk size比较大,也许VLLM已经填满了大部分chunk size,那么其实就没必要load了)。
内存拷贝:从storage_manager拿到一个chunk的CPU KV内存(MixedMemoryAllocator里面分配的是pin_memory)后,使用了一个自定义CUDA算子(csrc\mem_kernels.cu中的multi_layer_kv_transfer)拷贝到GPU KV cache里面:
class LMCacheEngine:
def retrieve( self, tokens: torch.Tensor, mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None, **kwargs,) -> torch.Tensor:
for start, end, key in self.token_database.process_tokens(tokens, mask):
assert isinstance(key, CacheEngineKey)
# Get the memory object from the storage backend
memory_obj = self.storage_manager.get(key)
if memory_obj is None:
if self.enable_p2p:
future_memory_obj = asyncio.run_coroutine_threadsafe(
self.distributed_server.issue_get(key),
self.distributed_loop,
)
memory_obj = future_memory_obj.result()
if memory_obj is None:
break
# NOTE(Jiayi): memory_obj doesn't have to be a pinned
# cpu tensor for the sake of performance.
# For example, disk->gpu is faster than disk->cpu->gpu.
# RDMA is another example.
self.gpu_connector.to_gpu(memory_obj, start, end, **kwargs)
memory_obj.ref_count_down()
class VLLMPagedMemGPUConnectorV2(GPUConnectorInterface):
@_lmcache_nvtx_annotate
def to_gpu(self, memory_obj: MemoryObj, start: int, end: int, **kwargs):
"""Expect a kwarg 'kvcaches' which is a nested tuple of K and V tensors.
The kvcaches should correspond to the "WHOLE token sequence".
"""
if memory_obj.metadata.fmt != MemoryFormat.KV_2LTD:
raise ValueError(
"The memory object should be in KV_2LTD format in order to be processed by VLLMPagedMemGPUConnector")
kvcaches: List[torch.Tensor] = kwargs["kvcaches"]
slot_mapping: torch.Tensor = kwargs["slot_mapping"]
kv_cache_pointers = self._initialize_pointers(kvcaches)
lmc_ops.multi_layer_kv_transfer(
memory_obj.tensor,
kv_cache_pointers,
slot_mapping[start:end],
kvcaches[0].device,
self.page_buffer_size,
False,
False,)
最后一个chunk不满一整个chunk的是按照实际的大小进行拷贝的。
slot_mapping是什么?
In vLLM, slot_mapping is a list or tensor that maps each token in a sequence to its corresponding slot in the key-value (KV) cache. Each entry in slot_mapping indicates the exact position (slot) in the cache where the token's key and value should be stored or retrieved, based on the block table and block size. This mapping is essential for efficient memory management and fast attention computation during inference and decoding, especially with paged or block-based KV cache layouts. See vllm.attention.backends.utils.compute_slot_mapping and source code.
slot_mapping是每个token在kv cache上面的全局存储位置。
const int slot_idx = slot_mapping[token_idx];
const int block_idx = slot_idx / block_size;
const int block_offset = slot_idx % block_size;KV store内存操作
基本上是load的逆操作:先分配一个chunk的CPU内存,然后使用一个CUDA算子把KV cache从GPU里面读取到这个CPU内存里面。最后StorageManager的cpu backend直接存储chunk的hash和这个kv内存。其他后端如disk则会根据这个内存写入到文件。
class LMCacheEngine:
@_lmcache_nvtx_annotate
@torch.inference_mode()
def store(self, tokens: torch.Tensor, mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,**kwargs,) -> None:
# FIXME(ApostaC): A HACK for distributed storage manager
if self.use_distributed_storage_manager:
self.store_distributed(tokens, mask, **kwargs)
return
if mask is not None:
num_stored_tokens = torch.sum(mask).item()
else:
num_stored_tokens = len(tokens)
monitor_req_id = self.stats_monitor.on_store_request(num_stored_tokens)
for start, end, key in self.token_database.process_tokens(tokens, mask):
assert isinstance(key, CacheEngineKey)
if self.storage_manager.contains(key):
continue
# Allocate the memory object
num_tokens = end - start
kv_shape = self.gpu_connector.get_shape(num_tokens)
kv_dtype = self.metadata.kv_dtype
memory_obj = self.storage_manager.allocate(kv_shape, kv_dtype)
if memory_obj is None:
logger.warning("Failed to allocate memory for the KV cache. The KV cache will not be stored.")
break
self.gpu_connector.from_gpu(memory_obj, start, end, **kwargs)
self.storage_manager.put(key, memory_obj)
# Update lookup server
if self.lookup_server is not None:
self.lookup_server.insert(key)
self.stats_monitor.on_store_finished(monitor_req_id)
logger.debug(f"Stored {num_stored_tokens} out of total {len(tokens)} tokens")
StorageManager
put
对每个backend都进行了put:
def put(self, key: CacheEngineKey, memory_obj: MemoryObj) -> None:
"""
Non-blocking function to put the memory object into the storages.
Do not store if the same object is being stored (handled here by
storage manager) or has been stored (handled by storage backend).
"""
# TODO(Jiayi): currently, the entire put task will be cancelled
# if one of the backend is already storing this cache.
# This might not be ideal. We need a caching policy to
# configure caching policies (e.g., write-through,
# write-back, etc.)
for storage_backend in self.storage_backends.values():
if storage_backend.exists_in_put_tasks(key) or storage_backend.contains(key):
memory_obj.ref_count_down()
return
# ever_put = False
for backend_name, backend in self.storage_backends.items():
put_task = backend.submit_put_task(key, memory_obj)
if put_task is None:
continue
memory_obj.ref_count_down()
put后边backend submit_put_task采用 asyncio异步操作,无需等待完成就返回。
get
首先从prefetch里面看看有没有预取任务,有的话等待一段时间。可以利用这个prefetch做一些load的优化。
然后从每个storage backend逐个去看有没可以匹配的,如果有就获取kv cache。
如果CPU backend没有却从别的backend获取到,就顺便也写入到CPU backend以便下次更快获取. get调用的是blocking读取接口。
def get(self, key: CacheEngineKey) -> Optional[MemoryObj]:
"""
Blocking function to get the memory object from the storages.
"""
# Search in prefetch task
self.manager_lock.acquire()
prefetch_task = self.prefetch_tasks.get(key, None)
self.manager_lock.release()
# Wait until prefetch task finishes
# Here, it is assumed all prefetch tasks load the memoryobj to
# hot cache (pinned cpu buffer)
if prefetch_task is not None:
logger.debug("Waiting for prefetching result. Optimally, this should not happen.")
# Calling result() twice (already once in callback) will have
# no effect
# Tune the timeout for better performance
prefetch_task.result(timeout=1)
# Search all backends for blocking get
for backend_name, backend in self.storage_backends.items():
# NOTE(Jiayi): bypass the allocator for now
memory_obj = backend.get_blocking(key)
if memory_obj is not None:
if backend_name != "LocalCPUBackend":
local_cpu_backend = self.storage_backends["LocalCPUBackend"]
assert isinstance(local_cpu_backend, LocalCPUBackend)
local_cpu_backend.write_back(key, memory_obj)
return memory_obj
return None
allocate
memory_allocator来自于LMCacheEngineBuilder._Create_memory_allocator为LMCacheEngine的MixedMemoryAllocator,这里面创建了一个pin_memory使用TensorMemoryAllocator进行分配:
class MixedMemoryAllocator(MemoryAllocatorInterface):
"""
Allocates (1) memory in the pre-allocated pinned memory.
(2) byte_array buffer memory.
"""
def __init__(self, size: int):
"""
:param int size: The size of the pinned memory in bytes.
"""
buffer = torch.empty(size, dtype=torch.uint8, pin_memory=True)
self.pin_allocator = TensorMemoryAllocator(buffer)
self.buffer_allocator = BufferAllocator("cpu")
self.host_mem_lock = threading.Lock()
def allocate(self, shape: Union[torch.Size, Tuple[int, ...]], dtype: Optional[torch.dtype], fmt: MemoryFormat = MemoryFormat.KV_2LTD) -> Optional[MemoryObj]:
if fmt == MemoryFormat.BINARY_BUFFER:
return self.buffer_allocator.allocate(shape, dtype, fmt)
elif fmt in [ MemoryFormat.KV_2LTD, MemoryFormat.KV_T2D, MemoryFormat.KV_MLA_FMT,]:
with self.host_mem_lock:
return self.pin_allocator.allocate(shape, dtype, fmt, self)
else:
raise ValueError(f"Unsupported memory format: {fmt}")
class TensorMemoryAllocator(MemoryAllocatorInterface):
"""
Implements a "explicit list" memory allocator.
"""
TensorMemoryAllocator工作原理
Implements a "explicit list" memory allocator.
初始化时的空闲块只有1个,就是整个内存块。
分配时,遍历 explicit_list (按起始地址排序的空闲块列表),寻找第一个大小大于等于 aligned_size 的空闲块,然后分配的就是这个空闲块开始的内存部分。并且把原来的空闲块删除,增加一个去掉分配后部分的空闲块。若未找到合适块,返回 None 并记录警告日志。
释放时,会把当前释放的块与前后空闲块进行合并。
MemoryObj引用计数管理
TensorMemoryObj的MemoryObjMetadata对象里面包括了一个引用计数,这个用于内存的释放管理。引用计数不为0说明正在被使用,例如被CPU-GPU之间的数据拷贝,backend的读写。引用计数为0,那么可以被驱逐,但是内存足够的情况下,仍然可以被保留用作下次匹配。
首先TensorMemoryAllocator allocate创建内存对象时引用计数已经被设为1。
Store时,StorageManager在put或者batched_put完成后,会对引用次数减1,但是除了CPU backend以外的store都是异步操作,因此这些backend在put之前会再次加1,完成后减1。因此只有这些backend写入完成后,引用计数才会变为0。
Load时,CPU backend如果有缓存,会对返回的引用计数加1。而其他后端则是先allocate,再拷贝进来。最后这个MemoryObj拷贝到GPU完成加载后,引用计数减1。
StorageManager backend
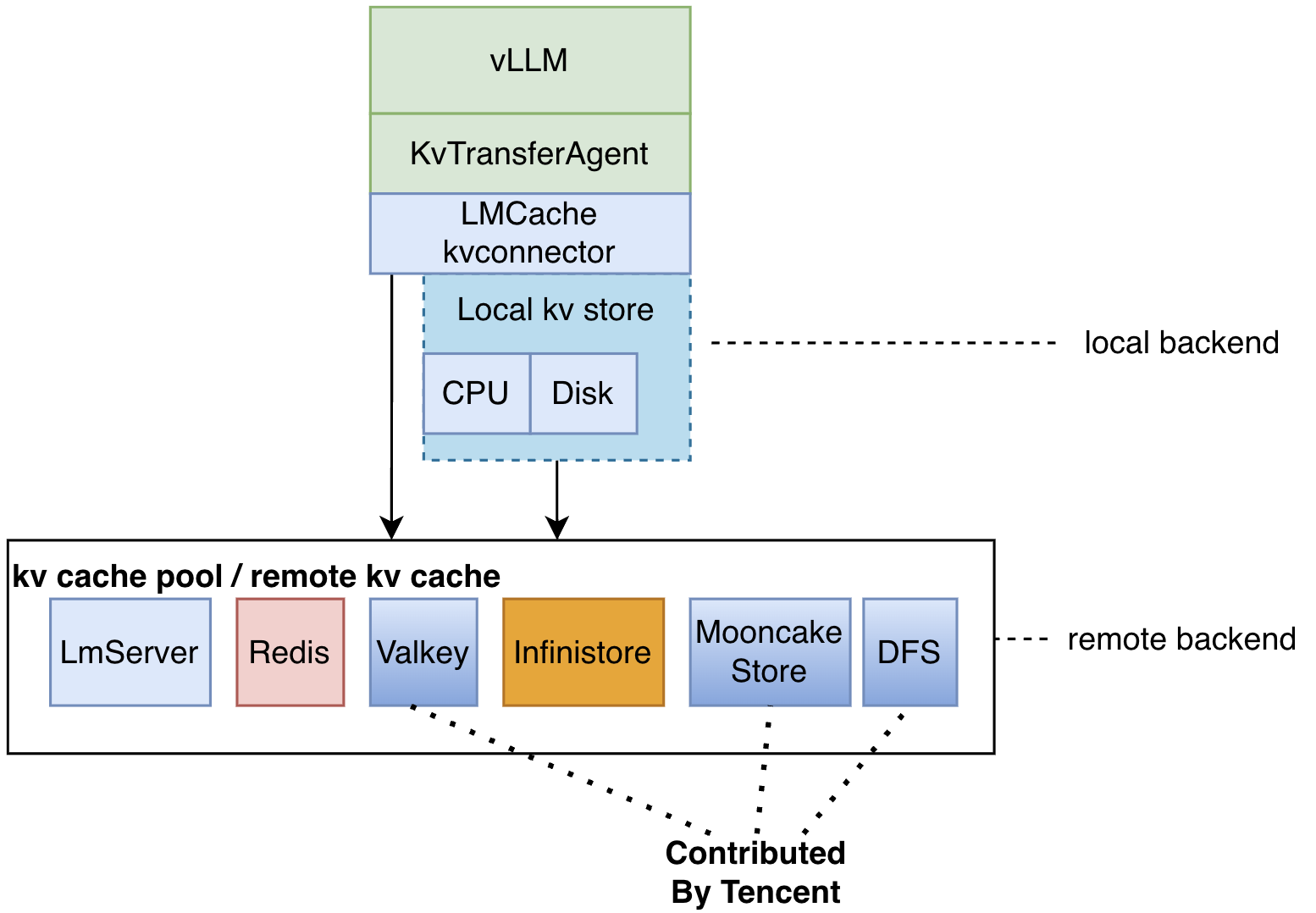
LocalCPUBackend
提前创建一个pin memory用于分配内存,然后使用dict进行存储key, value的映射关系。
kv cache驱逐策略
CPU的backend采用了一个特殊的驱逐策略。当CPU的内存被分配完的时候,采用循环从hot_cache(是一个order dict)里面依次遍历,找到一个ref_count为0的内存块进行释放,然后再次尝试分配,如果分配成功就退出循环。
另外CPU的backend get时,会把get到的cache放到hot_cache末尾,从而优先释放最不常用的部分。
LocalDiskBackend
每次打开一个文件存放kv chunk,使用_key_to_path获取文件路径。
async def async_save_bytes_to_disk(self, key: CacheEngineKey, memory_obj: MemoryObj) -> None:
"""
Convert KV to bytes and async store bytes to disk.
"""
path = self._key_to_path(key)
async with aiofiles.open(path, "wb") as f:
await f.write(byte_array)
self.insert_key(key, memory_obj)
memory_obj.ref_count_down()
self.disk_lock.acquire()
self.put_tasks.remove(key)
self.disk_lock.release()
def submit_put_task(self, key: CacheEngineKey, memory_obj: MemoryObj) -> Optional[Future]:
assert memory_obj.tensor is not None
# Update cache recency
evict_keys, put_status = self.evictor.update_on_put(
self.dict, memory_obj.get_physical_size()
)
if put_status == PutStatus.ILLEGAL:
return None
# evict caches
for evict_key in evict_keys:
self.remove(evict_key)
if self.lookup_server is not None:
self.lookup_server.batched_remove(evict_keys)
memory_obj.ref_count_up()
self.disk_lock.acquire()
self.put_tasks.append(key)
self.disk_lock.release()
future = asyncio.run_coroutine_threadsafe(
self.async_save_bytes_to_disk(key, memory_obj), self.loop
)
return future
驱逐实现了一个简单的LRUEvictor,同样是利用一个order dict,命中的时候把key移动到末尾。驱逐从前往后驱逐。被pin保护的不驱逐。
NixlBackend
当前用于PD之间的数据传输。
RemoteBackend
可以进一步卸载kv cache到remote backend,如mooncake store。
LMCache配置
yaml配置文件一些常用的参数设置,参考lmcache\v1\config.py
lmcache\v1\storage_backend\__init__.py中CreateStorageBackends会根据这些配置创建相应的backend。
lmcache\v1\storage_backend\connector\__init__.py的CreateConnector根据remote_url创建remote connector。
chunk_size: 256
max_local_cpu_size: 100 # in GB. CPU memory size of local CPU backend,每个TP独立
local_disk: Optional[str] # disk offload的文件夹路径
max_local_disk_size: float # in GB
remote_url: "" # 根据remote_url启动remote backend
save_unfull_chunk: false
# local_cpu: false # disable cpu offload
# PD传输的NIXL配置等等
火山引擎开发者社区是火山引擎打造的AI技术生态平台,聚焦Agent与大模型开发,提供豆包系列模型(图像/视频/视觉)、智能分析与会话工具,并配套评测集、动手实验室及行业案例库。社区通过技术沙龙、挑战赛等活动促进开发者成长,新用户可领50万Tokens权益,助力构建智能应用。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献5条内容
已为社区贡献5条内容






所有评论(0)