BERT 模型微调:GLUE 与 SQuAD 任务
本文详细介绍了如何在 PyTorch 中对 BERT 模型进行微调,以适应 GLUE 和 SQuAD 两类下游任务。内容涵盖了基于 BERT 构建分类和问答模型的步骤、训练循环的实现方法、数据集的处理及批量化策略,以及模型输出与损失函数的使用。通过本文,读者可以掌握在实际 NLP 任务中微调 BERT 的完整流程,并理解不同任务对模型输入输出的具体要求。
【精选优质专栏推荐】
- 《AI 技术前沿》 —— 紧跟 AI 最新趋势与应用
- 《网络安全新手快速入门(附漏洞挖掘案例)》 —— 零基础安全入门必看
- 《BurpSuite 入门教程(附实战图文)》 —— 渗透测试必备工具详解
- 《网安渗透工具使用教程(全)》 —— 一站式工具手册
- 《CTF 新手入门实战教程》 —— 从题目讲解到实战技巧
- 《前后端项目开发(新手必知必会)》 —— 实战驱动快速上手
每个专栏均配有案例与图文讲解,循序渐进,适合新手与进阶学习者,欢迎订阅。

前言
BERT 是一个被训练用于理解语言的基础 NLP 模型,但它可能无法直接用于任何特定任务。然而,你可以通过添加合适的模型头并针对特定任务进行训练来构建 BERT。这一过程称为微调。在本文中,你将学习如何针对多个 NLP 任务微调一个 BERT 模型。
本文分为两部分:
- 针对 GLUE 任务微调 BERT 模型
- 针对 SQuAD 任务微调 BERT 模型
针对 GLUE 任务微调 BERT 模型
GLUE 是一个用于评估自然语言理解(NLU)任务的基准。它包含 9 个任务,例如情感分析、复述识别和文本分类。模型从示例中学习任务特定的行为。GLUE 有一个保留的测试集,用于评估模型在每个任务上的性能,并在公共排行榜上公布结果。
让我们以 GLUE 中的 “sst2” 任务(情感分类)为例。
你可以使用 Hugging Face datasets 库加载该数据集:
from datasets import load_dataset
task = "sst2" # sentiment classification
dataset = load_dataset("glue", task)
print("Train size:", len(dataset["train"]))
print("Validation size:", len(dataset["validation"]))
print("Test size:", len(dataset["test"]))
# print one sample
print(dataset["train"][42])
运行此代码,输出为:
Train size: 67349
Validation size: 872
Test size: 1821
{'sentence': "as they come , already having been recycled more times than i 'd care to
count ", 'label': 0, 'idx': 42}
加载的数据集有三个划分:train、validation 和 test。数据集中的每个样本都是一个字典。我们关心的键是 “sentence” 和 “label”。“label” 是 0 或 1,分别代表负面或正面情感。
此数据集不能直接使用,因为你需要将文本句子转换为 token 序列。此外,训练循环需要批量数据,因此你需要创建随机打乱并填充后的序列批次。让我们使用一个自定义的 collate 函数来创建一个 PyTorch DataLoader:
...
import torch
def collate(batch: list[dict], tokenizer: tokenizers.Tokenizer, max_len: int):
"""Custom collate function to handle variable-length sequences in dataset."""
cls_id = tokenizer.token_to_id("[CLS]")
sep_id = tokenizer.token_to_id("[SEP]")
pad_id = tokenizer.token_to_id("[PAD]")
sentences: list[str] = [item["sentence"] for item in batch]
labels = torch.tensor([item["label"] for item in batch])
input_ids = []
for sentence in sentences:
seq = [cls_id]
seq.extend(tokenizer.encode(sentence).ids)
if len(seq) >= max_len:
seq = seq[:max_len-1]
seq.append(sep_id)
num_pad = max_len - len(seq)
seq.extend([pad_id] * num_pad)
input_ids.append(seq)
input_ids = torch.tensor(input_ids, dtype=torch.long)
return input_ids, labels
batch_size = 16
max_len = 128
tokenizer = tokenizers.Tokenizer.from_file("wikitext-2_wordpiece.json")
collate_fn = functools.partial(collate, tokenizer=tokenizer, max_len=max_len)
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset["train"], batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True, collate_fn=collate_fn)
val_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset["validation"], batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=False, collate_fn=collate_fn)
collate() 函数将一个由字典组成的样本批次作为输入。它将文本句子转换为 token 序列,并填充到相同长度。与 BERT 预训练不同,你没有句子对,但仍需要使用 [CLS] 和 [SEP] 作为输出序列的分隔符。collate 函数的输出是两个张量组成的元组:一个是 2D 的输入 ID,另一个是 1D 的标签。
你设置了两个 DataLoader:一个用于训练集,一个用于验证集。训练集被随机打乱,而验证集不会。
接下来,你需要为 GLUE 任务设置一个模型。由于这是一个句子分类任务,你只需在 BERT 模型顶部添加一个线性层,将 [CLS] token 的隐藏状态映射到标签数量。下面是实现:
...
class BertForSequenceClassification(nn.Module):
"""BERT model for GLUE tasks."""
def __init__(self, config: BertConfig, num_labels: int):
super().__init__()
self.bert = BertModel(config)
self.classifier = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, num_labels)
def forward(self, input_ids: torch.Tensor, pad_id: int = 0) -> torch.Tensor:
# pooled_output corresponds to the [CLS] token
token_type_ids = torch.zeros_like(input_ids)
seq_output, pooled_output = self.bert(input_ids, token_type_ids, pad_id=pad_id)
logits = self.classifier(pooled_output)
return logits
在 BertForSequenceClassification 类中,你使用基础 BERT 模型处理输入序列。[CLS] token 对应的 pooled output 随后传入线性层,映射到标签数量。sequence output 则未使用。模型的输出是分类任务的 logits。在情感分类的情况下,每个样本会对应一个包含两个值的向量。
所有 BERT 微调都遵循类似的架构。事实上,你可以在下方来自 BERT 论文的图中看到,你正在使用架构 (b):
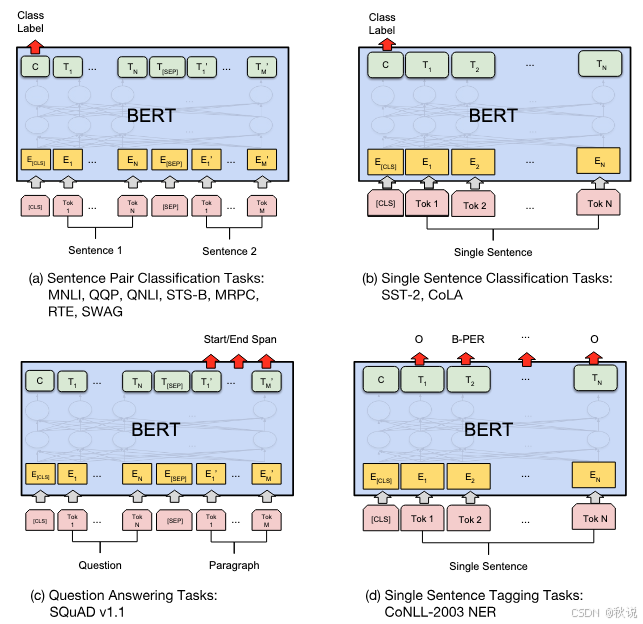
由于你已经训练了基础 BERT 模型,你可以实例化用于序列分类的模型,然后加载基础模型的预训练权重:
...
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
config = BertConfig()
model = BertForSequenceClassification(config, num_labels)
model.to(device)
model.bert.load_state_dict(torch.load("bert_model.pth", map_location=device))
现在你可以运行训练循环。与预训练相比,微调只需要几个 epoch。除此之外,训练循环相当典型:
..
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=2e-5)
num_epochs = 3
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
model.train()
# Training
with tqdm.tqdm(train_loader, desc=f"Epoch {epoch+1}/{num_epochs}") as pbar:
for batch in pbar:
# get batched data
input_ids, labels = batch
input_ids = input_ids.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
# forward pass
logits = model(input_ids, torch.zeros_like(input_ids))
# backward pass
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss = loss_fn(logits, labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# update progress bar
pbar.set_postfix(loss=float(loss))
pbar.update(1)
# Validation: Keep track of the average loss and accuracy
model.eval()
val_loss, num_matches, num_batches, num_samples = 0, 0, 0, 0
with torch.no_grad():
for batch in val_loader:
# get batched data
input_ids, labels = batch
input_ids = input_ids.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
# forward pass on validation data
logits = model(input_ids)
# compute loss
loss = loss_fn(logits, labels)
val_loss += loss.item()
num_batches += 1
# compute accuracy
predictions = logits.argmax(dim=-1)
num_matches += (predictions == labels).sum().item()
num_samples += len(labels)
avg_loss = val_loss / num_batches
acc = num_matches / num_samples
print(f"Validation {epoch+1}/{num_epochs}: acc {acc:.4f}, avg loss {avg_loss:.4f}")
运行此代码,你可能会看到:
Epoch 1/3: 100%|██████████████████████████| 4210/4210 [02:14<00:00, 31.37it/s, loss=0.844]
Validation 1/3: acc 0.5092, avg loss 0.7097
Epoch 2/3: 100%|██████████████████████████| 4210/4210 [02:13<00:00, 31.46it/s, loss=0.591]
Validation 2/3: acc 0.5092, avg loss 0.7164
Epoch 3/3: 100%|██████████████████████████| 4210/4210 [02:13<00:00, 31.51it/s, loss=0.699]
Validation 3/3: acc 0.5092, avg loss 0.6932
由于你同时拥有训练集和验证集,你使用训练集进行训练,然后在验证集上进行评估。务必使用 model.train() 和 model.eval() 将模型分别设置为训练模式或评估模式,因为你的模型使用了 dropout 层。
这就是你在 GLUE 任务上微调 BERT 模型所需要做的一切。下面是用于序列分类的完整代码:
import dataclasses
import functools
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import tqdm
from datasets import load_dataset
from tokenizers import Tokenizer
from torch import Tensor
# BERT config and model defined previously
@dataclasses.dataclass
class BertConfig:
"""Configuration for BERT model."""
vocab_size: int = 30522
num_layers: int = 12
hidden_size: int = 768
num_heads: int = 12
dropout_prob: float = 0.1
pad_id: int = 0
max_seq_len: int = 512
num_types: int = 2
class BertBlock(nn.Module):
"""One transformer block in BERT."""
def __init__(self, hidden_size: int, num_heads: int, dropout_prob: float):
super().__init__()
self.attention = nn.MultiheadAttention(hidden_size, num_heads,
dropout=dropout_prob, batch_first=True)
self.attn_norm = nn.LayerNorm(hidden_size)
self.ff_norm = nn.LayerNorm(hidden_size)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout_prob)
self.feed_forward = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(hidden_size, 4 * hidden_size),
nn.GELU(),
nn.Linear(4 * hidden_size, hidden_size),
)
def forward(self, x: Tensor, pad_mask: Tensor) -> Tensor:
# self-attention with padding mask and post-norm
attn_output, _ = self.attention(x, x, x, key_padding_mask=pad_mask)
x = self.attn_norm(x + attn_output)
# feed-forward with GeLU activation and post-norm
ff_output = self.feed_forward(x)
x = self.ff_norm(x + self.dropout(ff_output))
return x
class BertPooler(nn.Module):
"""Pooler layer for BERT to process the [CLS] token output."""
def __init__(self, hidden_size: int):
super().__init__()
self.dense = nn.Linear(hidden_size, hidden_size)
self.activation = nn.Tanh()
def forward(self, x: Tensor) -> Tensor:
x = self.dense(x)
x = self.activation(x)
return x
class BertModel(nn.Module):
"""Backbone of BERT model."""
def __init__(self, config: BertConfig):
super().__init__()
# embedding layers
self.word_embeddings = nn.Embedding(config.vocab_size, config.hidden_size,
padding_idx=config.pad_id)
self.type_embeddings = nn.Embedding(config.num_types, config.hidden_size)
self.position_embeddings = nn.Embedding(config.max_seq_len, config.hidden_size)
self.embeddings_norm = nn.LayerNorm(config.hidden_size)
self.embeddings_dropout = nn.Dropout(config.dropout_prob)
# transformer blocks
self.blocks = nn.ModuleList([
BertBlock(config.hidden_size, config.num_heads, config.dropout_prob)
for _ in range(config.num_layers)
])
# [CLS] pooler layer
self.pooler = BertPooler(config.hidden_size)
def forward(self, input_ids: Tensor, token_type_ids: Tensor, pad_id: int = 0,
) -> tuple[Tensor, Tensor]:
# create attention mask for padding tokens
pad_mask = input_ids == pad_id
# convert integer tokens to embedding vectors
batch_size, seq_len = input_ids.shape
position_ids = torch.arange(seq_len, device=input_ids.device).unsqueeze(0)
position_embeddings = self.position_embeddings(position_ids)
type_embeddings = self.type_embeddings(token_type_ids)
token_embeddings = self.word_embeddings(input_ids)
x = token_embeddings + type_embeddings + position_embeddings
x = self.embeddings_norm(x)
x = self.embeddings_dropout(x)
# process the sequence with transformer blocks
for block in self.blocks:
x = block(x, pad_mask)
# pool the hidden state of the `[CLS]` token
pooled_output = self.pooler(x[:, 0, :])
return x, pooled_output
# Define new BERT model for sequence classification
class BertForSequenceClassification(nn.Module):
"""BERT model for GLUE tasks."""
def __init__(self, config: BertConfig, num_labels: int):
super().__init__()
self.bert = BertModel(config)
self.classifier = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, num_labels)
def forward(self, input_ids: Tensor, pad_id: int = 0) -> Tensor:
# pooled_output corresponds to the [CLS] token
token_type_ids = torch.zeros_like(input_ids)
seq_output, pooled_output = self.bert(input_ids, token_type_ids, pad_id=pad_id)
logits = self.classifier(pooled_output)
return logits
# Load GLUE dataset (e.g., 'sst2' for sentiment classification)
task = "sst2"
dataset = load_dataset("glue", task)
num_labels = 2 # dataset["train"]["label"] is either 0 or 1
# Load the pretrained BERT tokenizer
TOKENIZER_PATH = "wikitext-2_wordpiece.json"
tokenizer = Tokenizer.from_file(TOKENIZER_PATH)
# Setup dataloader for training and validation datasets
def collate(batch: list[dict], tokenizer: Tokenizer, max_len: int) -> tuple[Tensor, Tensor]:
"""Collate variable-length sequences in the dataset."""
cls_id = tokenizer.token_to_id("[CLS]")
sep_id = tokenizer.token_to_id("[SEP]")
pad_id = tokenizer.token_to_id("[PAD]")
sentences: list[str] = [item["sentence"] for item in batch]
labels = torch.tensor([item["label"] for item in batch])
input_ids = []
for sentence in sentences:
seq = [cls_id]
seq.extend(tokenizer.encode(sentence).ids)
if len(seq) >= max_len:
seq = seq[:max_len-1]
seq.append(sep_id)
num_pad = max_len - len(seq)
seq.extend([pad_id] * num_pad)
input_ids.append(seq)
input_ids = torch.tensor(input_ids, dtype=torch.long)
return input_ids, labels
batch_size = 16
max_len = 128
collate_fn = functools.partial(collate, tokenizer=tokenizer, max_len=max_len)
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset["train"], batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True, collate_fn=collate_fn)
val_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset["validation"], batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=False, collate_fn=collate_fn)
# Create classification model with a pretrained foundation BERT model
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
config = BertConfig()
model = BertForSequenceClassification(config, num_labels)
model.to(device)
model.bert.load_state_dict(torch.load("bert_model.pth", map_location=device))
# Training setup
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=2e-5)
num_epochs = 3
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
model.train()
# Training
with tqdm.tqdm(train_loader, desc=f"Epoch {epoch+1}/{num_epochs}") as pbar:
for batch in pbar:
# get batched data
input_ids, labels = batch
input_ids = input_ids.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
# forward pass
logits = model(input_ids, torch.zeros_like(input_ids))
# backward pass
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss = loss_fn(logits, labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# update progress bar
pbar.set_postfix(loss=float(loss))
pbar.update(1)
# Validation: Keep track of the average loss and accuracy
model.eval()
val_loss, num_matches, num_batches, num_samples = 0, 0, 0, 0
with torch.no_grad():
for batch in val_loader:
# get batched data
input_ids, labels = batch
input_ids = input_ids.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
# forward pass on validation data
logits = model(input_ids)
# compute loss
loss = loss_fn(logits, labels)
val_loss += loss.item()
num_batches += 1
# compute accuracy
predictions = logits.argmax(dim=-1)
num_matches += (predictions == labels).sum().item()
num_samples += len(labels)
avg_loss = val_loss / num_batches
acc = num_matches / num_samples
print(f"Validation {epoch+1}/{num_epochs}: acc {acc:.4f}, avg loss {avg_loss:.4f}")
# Save the fine-tuned model
torch.save(model.state_dict(), f"bert_model_glue_sst2.pth")
针对 SQuAD 任务微调 BERT 模型
SQuAD 是一个问答数据集。每个样本包含一个问题和一个上下文段落。问题的答案是出现在上下文段落中的一个词语片段。这并不是一个通用的问答任务,因为答案总是上下文中的一个子字符串。如果不存在这样的子字符串,则该问题没有答案。
让我们来看一下数据集中的一个样本:
from datasets import load_dataset
dataset = load_dataset("squad")
print("Train size:", len(dataset["train"]))
print("Validation size:", len(dataset["validation"]))
# print one sample
print(dataset["train"][42])
运行这段代码,输出为:
Train size: 87599
Validation size: 10570
{'id': '5733ae924776f41900661016', 'title': 'University_of_Notre_Dame',
'context': 'Notre Dame is known for its competitive admissions, ...',
'question': 'What percentage of students at Notre Dame participated in the Early
Action program?', 'answers': {'text': ['39.1%'], 'answer_start': [488]}}
SQuAD 数据集只有训练集和验证集两个部分。每个样本是一个字典,包含键 “id”、“title”、“context”、“question” 和 “answers”。“answers” 键是一个字典,包含答案文本及其在上下文中的偏移位置。
要训练模型,你需要像处理 GLUE 任务那样,将数据样本批处理并转换为张量。让我们为 SQuAD 数据集创建一个自定义的 collate 函数:
def collate(batch: list[dict], tokenizer: tokenizers.Tokenizer, max_len: int):
cls_id = tokenizer.token_to_id("[CLS]")
sep_id = tokenizer.token_to_id("[SEP]")
pad_id = tokenizer.token_to_id("[PAD]")
input_ids_list = []
token_type_ids_list = []
start_positions = []
end_positions = []
for item in batch:
# Tokenize question and context
question, context = item["question"], item["context"]
question_ids = tokenizer.encode(question).ids
context_ids = tokenizer.encode(context).ids
# Build input: [CLS] question [SEP] context [SEP]
input_ids = [cls_id, *question_ids, sep_id, *context_ids, sep_id]
token_type_ids = [0] * (len(question_ids)+2) + [1] * (len(context_ids)+1)
# Truncate or pad to max length
if len(input_ids) > max_len:
input_ids = input_ids[:max_len]
token_type_ids = token_type_ids[:max_len]
else:
input_ids.extend([pad_id] * (max_len - len(input_ids)))
token_type_ids.extend([1] * (max_len - len(token_type_ids)))
# Find answer position in tokens: Answer may not be in the context
start_pos = end_pos = 0
if len(item["answers"]["text"]) > 0:
answers = tokenizer.encode(item["answers"]["text"][0]).ids
# find the context offset of the answer in context_ids
for i in range(len(context_ids) - len(answers) + 1):
if context_ids[i:i+len(answers)] == answers:
start_pos = i + len(question_ids) + 2
end_pos = start_pos + len(answers) - 1
break
if end_pos >= max_len:
start_pos = end_pos = 0 # answer is clipped, hence no answer
input_ids_list.append(input_ids)
token_type_ids_list.append(token_type_ids)
start_positions.append(start_pos)
end_positions.append(end_pos)
input_ids_list = torch.tensor(input_ids_list)
token_type_ids_list = torch.tensor(token_type_ids_list)
start_positions = torch.tensor(start_positions)
end_positions = torch.tensor(end_positions)
return (input_ids_list, token_type_ids_list, start_positions, end_positions)
batch_size = 16
max_len = 384 # Longer for Q&A to accommodate context
collate_fn = functools.partial(collate, tokenizer=tokenizer, max_len=max_len)
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset["train"], batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True, collate_fn=collate_fn)
val_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset["validation"], batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=False, collate_fn=collate_fn)
这个 collate 函数比 GLUE 任务的更复杂,因为你需要将两个句子按 [CLS] question [SEP] context [SEP] 的格式作为输入。context 可能会因为最大长度限制而被截断。问题、上下文和答案都会被转换为 token 序列。在内部循环中,你会在上下文中找到答案片段的位置。如果答案在提供的上下文中找不到,你会将该问题标记为无答案。
collate 函数最重要的作用之一,是为一个 batch 创建张量。这里你生成了四个张量:输入(包括问题和上下文)、token type IDs(标记哪些 token 属于问题,哪些属于上下文),以及答案片段的起始位置和结束位置。
接下来,你需要为 SQuAD 任务设置一个模型。策略是处理 BERT 模型的序列输出,使得序列中的每个 token 都被转换为成为答案起点或终点的概率。然后,你可以找到概率最高的起始和结束 token 来组成答案片段。实现非常直接:
class BertForQuestionAnswering(nn.Module):
"""BERT model for SQuAD question answering."""
def __init__(self, config):
super().__init__()
self.bert = BertModel(config)
# Two outputs: start and end position logits
self.qa_outputs = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, 2)
def forward(self, input_ids, token_type_ids, pad_id: int = 0):
# Get sequence output from BERT (batch_size, seq_len, hidden_size)
seq_output, pooled_output = self.bert(input_ids, token_type_ids, pad_id=pad_id)
# Project to start and end logits
logits = self.qa_outputs(seq_output) # (batch_size, seq_len, 2)
start_logits = logits[:, :, 0] # (batch_size, seq_len)
end_logits = logits[:, :, 1] # (batch_size, seq_len)
return start_logits, end_logits
基础 BERT 模型会产生序列输出和池化输出。对于 SQuAD 任务,你仅使用序列输出。你将该输出传入一个线性层以生成起始和结束位置的 logits,并分别返回它们。要将这些 logits 转换为概率,你需要对它们应用 softmax 函数,这可以在模型外部完成。
如同上面 GLUE 任务示例中所示,你可以实例化模型并加载预训练权重:
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
config = BertConfig()
model = BertForQuestionAnswering(config)
model.to(device)
model.bert.load_state_dict(torch.load("bert_model.pth", map_location=device))
最后,你可以运行用于微调的训练循环:
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=2e-5)
num_epochs = 3
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
model.train()
# Training
with tqdm.tqdm(train_loader, desc=f"Epoch {epoch+1}/{num_epochs}") as pbar:
for batch in pbar:
# get batched data
input_ids, token_type_ids, start_positions, end_positions = batch
input_ids = input_ids.to(device)
token_type_ids = token_type_ids.to(device)
start_positions = start_positions.to(device)
end_positions = end_positions.to(device)
# forward pass
start_logits, end_logits = model(input_ids, token_type_ids)
# backward pass
optimizer.zero_grad()
start_loss = loss_fn(start_logits, start_positions)
end_loss = loss_fn(end_logits, end_positions)
loss = start_loss + end_loss
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# update progress bar
pbar.set_postfix(loss=float(loss))
pbar.update(1)
# Validation: Keep track of the average loss and accuracy
model.eval()
val_loss, num_matches, num_batches, num_samples = 0, 0, 0, 0
with torch.no_grad():
for batch in val_loader:
# get batched data
input_ids, token_type_ids, start_positions, end_positions = batch
input_ids = input_ids.to(device)
token_type_ids = token_type_ids.to(device)
start_positions = start_positions.to(device)
end_positions = end_positions.to(device)
# forward pass on validation data
start_logits, end_logits = model(input_ids, token_type_ids)
# compute loss
start_loss = loss_fn(start_logits, start_positions)
end_loss = loss_fn(end_logits, end_positions)
loss = start_loss + end_loss
val_loss += loss.item()
num_batches += 1
# compute accuracy
pred_start = start_logits.argmax(dim=-1)
pred_end = end_logits.argmax(dim=-1)
match = (pred_start == start_positions) & (pred_end == end_positions)
num_matches += match.sum().item()
num_samples += len(start_positions)
avg_loss = val_loss / num_batches
acc = num_matches / num_samples
print(f"Validation {epoch+1}/{num_epochs}: acc {acc:.4f}, avg loss {avg_loss:.4f}")
训练循环与 GLUE 任务的类似。不同之处在于你现在使用序列中每个 token 对应的输出,而不是使用 pooled output。具有最高 logit 值的 token 是预测的起始或结束位置。损失函数是预测起始和结束位置的交叉熵损失之和。
这是一种简化的使用模型输出的方式。你可以在约束结束位置大于等于起始位置的前提下,通过寻找具有最高组合得分的起始-结束对来优化逻辑,从而可能提升模型的性能。
运行这段代码,你可能会看到:
Epoch 1/3: 100%|████████████████████████████| 5475/5475 [07:45<00:00, 11.77it/s, loss=9.7]
Validation 1/3: acc 0.0189, avg loss 8.6972
Epoch 2/3: 100%|███████████████████████████| 5475/5475 [07:44<00:00, 11.78it/s, loss=8.37]
Validation 2/3: acc 0.0358, avg loss 8.2596
Epoch 3/3: 100%|███████████████████████████| 5475/5475 [07:44<00:00, 11.78it/s, loss=7.85]
Validation 3/3: acc 0.0449, avg loss 7.9882
你可能会注意到模型的表现并不理想。这很可能是因为基础 BERT 模型是在更小的 WikiText-2 数据集上训练的,无法很好泛化到更复杂的任务上。为了在实际应用中获得更好的性能,你应该使用官方预训练权重。
下面是用于在 SQuAD 任务上微调 BERT 模型的完整代码:
import collections
import dataclasses
import functools
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import tqdm
from datasets import load_dataset
from tokenizers import Tokenizer
from torch import Tensor
# BERT config and model defined previously
@dataclasses.dataclass
class BertConfig:
"""Configuration for BERT model."""
vocab_size: int = 30522
num_layers: int = 12
hidden_size: int = 768
num_heads: int = 12
dropout_prob: float = 0.1
pad_id: int = 0
max_seq_len: int = 512
num_types: int = 2
class BertBlock(nn.Module):
"""One transformer block in BERT."""
def __init__(self, hidden_size: int, num_heads: int, dropout_prob: float):
super().__init__()
self.attention = nn.MultiheadAttention(hidden_size, num_heads,
dropout=dropout_prob, batch_first=True)
self.attn_norm = nn.LayerNorm(hidden_size)
self.ff_norm = nn.LayerNorm(hidden_size)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout_prob)
self.feed_forward = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(hidden_size, 4 * hidden_size),
nn.GELU(),
nn.Linear(4 * hidden_size, hidden_size),
)
def forward(self, x: Tensor, pad_mask: Tensor) -> Tensor:
# self-attention with padding mask and post-norm
attn_output, _ = self.attention(x, x, x, key_padding_mask=pad_mask)
x = self.attn_norm(x + attn_output)
# feed-forward with GeLU activation and post-norm
ff_output = self.feed_forward(x)
x = self.ff_norm(x + self.dropout(ff_output))
return x
class BertPooler(nn.Module):
"""Pooler layer for BERT to process the [CLS] token output."""
def __init__(self, hidden_size: int):
super().__init__()
self.dense = nn.Linear(hidden_size, hidden_size)
self.activation = nn.Tanh()
def forward(self, x: Tensor) -> Tensor:
x = self.dense(x)
x = self.activation(x)
return x
class BertModel(nn.Module):
"""Backbone of BERT model."""
def __init__(self, config: BertConfig):
super().__init__()
# embedding layers
self.word_embeddings = nn.Embedding(config.vocab_size, config.hidden_size,
padding_idx=config.pad_id)
self.type_embeddings = nn.Embedding(config.num_types, config.hidden_size)
self.position_embeddings = nn.Embedding(config.max_seq_len, config.hidden_size)
self.embeddings_norm = nn.LayerNorm(config.hidden_size)
self.embeddings_dropout = nn.Dropout(config.dropout_prob)
# transformer blocks
self.blocks = nn.ModuleList([
BertBlock(config.hidden_size, config.num_heads, config.dropout_prob)
for _ in range(config.num_layers)
])
# [CLS] pooler layer
self.pooler = BertPooler(config.hidden_size)
def forward(self, input_ids: Tensor, token_type_ids: Tensor, pad_id: int = 0,
) -> tuple[Tensor, Tensor]:
# create attention mask for padding tokens
pad_mask = input_ids == pad_id
# convert integer tokens to embedding vectors
batch_size, seq_len = input_ids.shape
position_ids = torch.arange(seq_len, device=input_ids.device).unsqueeze(0)
position_embeddings = self.position_embeddings(position_ids)
type_embeddings = self.type_embeddings(token_type_ids)
token_embeddings = self.word_embeddings(input_ids)
x = token_embeddings + type_embeddings + position_embeddings
x = self.embeddings_norm(x)
x = self.embeddings_dropout(x)
# process the sequence with transformer blocks
for block in self.blocks:
x = block(x, pad_mask)
# pool the hidden state of the `[CLS]` token
pooled_output = self.pooler(x[:, 0, :])
return x, pooled_output
# Define new BERT model for question answering
class BertForQuestionAnswering(nn.Module):
"""BERT model for SQuAD question answering."""
def __init__(self, config: BertConfig):
super().__init__()
self.bert = BertModel(config)
# Two outputs: start and end position logits
self.qa_outputs = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, 2)
def forward(self,
input_ids: Tensor,
token_type_ids: Tensor,
pad_id: int = 0,
) -> tuple[Tensor, Tensor]:
# Get sequence output from BERT (batch_size, seq_len, hidden_size)
seq_output, pooled_output = self.bert(input_ids, token_type_ids, pad_id=pad_id)
# Project to start and end logits
logits = self.qa_outputs(seq_output) # (batch_size, seq_len, 2)
start_logits = logits[:, :, 0] # (batch_size, seq_len)
end_logits = logits[:, :, 1] # (batch_size, seq_len)
return start_logits, end_logits
# Load SQuAD dataset for question answering
dataset = load_dataset("squad")
# Load the pretrained BERT tokenizer
TOKENIZER_PATH = "wikitext-2_wordpiece.json"
tokenizer = Tokenizer.from_file(TOKENIZER_PATH)
# Setup collate function to tokenize question-context pairs for the model
def collate(batch: list[dict], tokenizer: Tokenizer, max_len: int,
) -> tuple[Tensor, Tensor, Tensor, Tensor]:
"""Collate question-context pairs for the model."""
cls_id = tokenizer.token_to_id("[CLS]")
sep_id = tokenizer.token_to_id("[SEP]")
pad_id = tokenizer.token_to_id("[PAD]")
input_ids_list = []
token_type_ids_list = []
start_positions = []
end_positions = []
for item in batch:
# Tokenize question and context
question, context = item["question"], item["context"]
question_ids = tokenizer.encode(question).ids
context_ids = tokenizer.encode(context).ids
# Build input: [CLS] question [SEP] context [SEP]
input_ids = [cls_id, *question_ids, sep_id, *context_ids, sep_id]
token_type_ids = [0] * (len(question_ids)+2) + [1] * (len(context_ids)+1)
# Truncate or pad to max length
if len(input_ids) > max_len:
input_ids = input_ids[:max_len]
token_type_ids = token_type_ids[:max_len]
else:
input_ids.extend([pad_id] * (max_len - len(input_ids)))
token_type_ids.extend([1] * (max_len - len(token_type_ids)))
# Find answer position in tokens: Answer may not be in the context
start_pos = end_pos = 0
if len(item["answers"]["text"]) > 0:
answers = tokenizer.encode(item["answers"]["text"][0]).ids
# find the context offset of the answer in context_ids
for i in range(len(context_ids) - len(answers) + 1):
if context_ids[i:i+len(answers)] == answers:
start_pos = i + len(question_ids) + 2
end_pos = start_pos + len(answers) - 1
break
if end_pos >= max_len:
start_pos = end_pos = 0 # answer is clipped, hence no answer
input_ids_list.append(input_ids)
token_type_ids_list.append(token_type_ids)
start_positions.append(start_pos)
end_positions.append(end_pos)
input_ids_list = torch.tensor(input_ids_list)
token_type_ids_list = torch.tensor(token_type_ids_list)
start_positions = torch.tensor(start_positions)
end_positions = torch.tensor(end_positions)
return (input_ids_list, token_type_ids_list, start_positions, end_positions)
batch_size = 16
max_len = 384 # Longer for Q&A to accommodate context
collate_fn = functools.partial(collate, tokenizer=tokenizer, max_len=max_len)
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset["train"], batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True, collate_fn=collate_fn)
val_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset["validation"], batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=False, collate_fn=collate_fn)
# Create Q&A model with a pretrained foundation BERT model
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
config = BertConfig()
model = BertForQuestionAnswering(config)
model.to(device)
model.bert.load_state_dict(torch.load("bert_model.pth", map_location=device))
# Training setup
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=2e-5)
num_epochs = 3
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
model.train()
# Training
with tqdm.tqdm(train_loader, desc=f"Epoch {epoch+1}/{num_epochs}") as pbar:
for batch in pbar:
# get batched data
input_ids, token_type_ids, start_positions, end_positions = batch
input_ids = input_ids.to(device)
token_type_ids = token_type_ids.to(device)
start_positions = start_positions.to(device)
end_positions = end_positions.to(device)
# forward pass
start_logits, end_logits = model(input_ids, token_type_ids)
# backward pass
optimizer.zero_grad()
start_loss = loss_fn(start_logits, start_positions)
end_loss = loss_fn(end_logits, end_positions)
loss = start_loss + end_loss
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# update progress bar
pbar.set_postfix(loss=float(loss))
pbar.update(1)
# Validation: Keep track of the average loss and accuracy
model.eval()
val_loss, num_matches, num_batches, num_samples = 0, 0, 0, 0
with torch.no_grad():
for batch in val_loader:
# get batched data
input_ids, token_type_ids, start_positions, end_positions = batch
input_ids = input_ids.to(device)
token_type_ids = token_type_ids.to(device)
start_positions = start_positions.to(device)
end_positions = end_positions.to(device)
# forward pass on validation data
start_logits, end_logits = model(input_ids, token_type_ids)
# compute loss
start_loss = loss_fn(start_logits, start_positions)
end_loss = loss_fn(end_logits, end_positions)
loss = start_loss + end_loss
val_loss += loss.item()
num_batches += 1
# compute accuracy
pred_start = start_logits.argmax(dim=-1)
pred_end = end_logits.argmax(dim=-1)
match = (pred_start == start_positions) & (pred_end == end_positions)
num_matches += match.sum().item()
num_samples += len(start_positions)
avg_loss = val_loss / num_batches
acc = num_matches / num_samples
print(f"Validation {epoch+1}/{num_epochs}: acc {acc:.4f}, avg loss {avg_loss:.4f}")
# Save the fine-tuned model
torch.save(model.state_dict(), f"bert_model_squad.pth")
总结
在本文中,你学习了如何对 BERT 模型进行 GLUE 和 SQuAD 任务的微调。具体来说,你学习了:
-
如何在 BERT 之上构建一个用于微调的新模型
-
如何运行微调所需的训练循环
-
GLUE 和 SQuAD 数据集以及它们对应的任务

火山引擎开发者社区是火山引擎打造的AI技术生态平台,聚焦Agent与大模型开发,提供豆包系列模型(图像/视频/视觉)、智能分析与会话工具,并配套评测集、动手实验室及行业案例库。社区通过技术沙龙、挑战赛等活动促进开发者成长,新用户可领50万Tokens权益,助力构建智能应用。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献13条内容
已为社区贡献13条内容





所有评论(0)